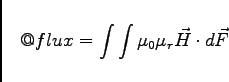symbol= QUAN_ISOL:
This is the full name of the symbol to be processed. This field has may be a 3D-E-field or a 3D-H-field.
quantity= QUAN:
This is the first part of the "symbol".
solution= ISOL:
This is the last part of the "symbol", the index of the "symbol".
normal= [x|y|z]:
The plane normal of the surface through which the flux integration shall be performed.
cutat= :
The
"normal" coordinate of the area through which the integration
shall be performed.
xlow= ??, xhigh= ??, ylow= ??, yhigh= ??, zlow= ??, zhigh= ??:
The coordinates of the rectangular area through which the flux integration shall be performed.
If
normal= x, the values xlow= ??, xhigh= ?? are ignored.
If
normal= y, the values ylow= ??, yhigh= ?? are ignored.
If
normal= z, the values zlow= ??, zhigh= ?? are ignored.
The actually used values will be slightly different from the specified ones. After
doit, the actually used values will be accessible as the symbolic
variables @cutat, @xlow, @xhigh, @ylow, @yhigh, @zlow, @zhigh.
doit:
The flux integration is performed, the result is shown in the menu. The result is available as the symbol
@flux for subsequent
calculations.
If the integrated field is an electric field, the result is
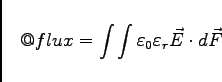
If the integrated field is a magnetic field, the result is