


Next: -gbor: A general body
Up: Geometric primitives
Previous: -gccylinder: A circular cylinder
Contents
A ggcylinder is a general cylinder with a footprint described
as a general polygon.
This footprint is swept along an axis in a general direction,
additionally, this footprint can shrink or expand along this axis,
additionally, this footprint can be rotated along the axis,
additionally, only parts of the ggcylinder that fulfill
some additional condition will be filled.
##############################################################################
# Flags: nomenu, noprompt, nomessage, #
##############################################################################
# section -ggcylinder #
##############################################################################
# material = 1 #
# whichcells = all, taboo= none #
# show = off -- (off | all | later | now) #
# name = ggcyl-000000000 #
# fixpoints= no -- (yes|no) #
# inside = yes -- (yes|no) #
# originprime = ( 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 ) #
# xprimedirection= ( 1.0, 0.0, 0.0 ) #
# yprimedirection= ( 0.0, 1.0, 0.0 ) #
# zprimedirection= ( 0.0, 0.0, 1.0 ) #
# usezprimedirection= no -- (yes|no) #
# range = ( undefined, undefined ) #
# pitch = 0.0 -- [degs/m] #
# xexpgrowth = 0.0 #
# yexpgrowth = 0.0 #
# xslope = 0.0 -- (x2/x1-1)/len [1/m] #
# yslope = 0.0 -- (y2/y1-1)/len [1/m] #
# xscaleprime= 1.0 #
# yscaleprime= 1.0 #
# zxscaletablefile= -none-
# zyscaletablefile= -none-
##############################################################################
## syntax: #
# point= (Xi, Yi) #
# arc, radius= RADIUS, type= [clockwise | counterclockwise] #
# size= [small | large ] #
# deltaphi= 5 #
# ellipse, center= (X0, Y0), size= [small | large ] #
# deltaphi= 5 #
##############################################################################
# doit, return, help, list, reset, clear #
##############################################################################
material=MAT:
The material index that will be assigned to cells inside the volume.
whichcells
Possible values are all, or a material-index.
If whichcells=all, all volume inside the
ggcylinder is assigned the material-index,
provided the former material is not taboo.
If whichcells is a material-index, only the parts of the
ggcylinder that are currently filled with the given index
are assigned the new material-index.
taboo
Possible values are none, or a material-index.
If taboo=none, all volume inside the
ggcylinder is assigned the material-index.
If taboo is a material-index, only the parts of the
ggcylinder that are currently filled with another index
than the given index are assigned the new material-index.
originprime:
The coordinates of the origin of the ggcylinder.
xprimedirection:
The direction of the x'-axis of the polygon that describes the footprint.
yprimedirection:
The direction of the y'-axis of the polygon that describes the footprint.
The y'-direction will internally be enforced to be perpendicular
to the x'-direction.
usezprimedirection= [yes|no]:
If usezprimedirection= yes, the axis of the cylinder is not
computed from the cross product of xprimedirection and yprimedirection,
but is taken to be the direction given by
zprimedirection= ( XZ, YZ, ZZ ).
zprimedirection= ( XZ, YZ, ZZ ):
If usezprimedirection= yes, the axis of the cylinder has the
direction given by zprimedirection= ( XZ, YZ, ZZ ).
If usezprimedirection= no, the given values are not used
and the direction is given by the cross product of
xprimedirection and yprimedirection.
range:
Start and end values of the z'-coordinate of the cylinder in the
coordinate system of xprimedirection,yprimedirection,(xprime
yprime), relative to
originprime.
pitch:
Phase in degrees/m.
The footprint will be rotated along the axis.
xexpgrowth, yexpgrowth
Alpha of the exponential growth of the x-coordinates, resp. y-coordinates of the footprint along the axis in 1/m.
xslope, yslope:
Factor of the linear growth of the x-coordinates, res. y-coordinates
of the footprint along the axis in 1/m.
xscaleprime, yscaleprime:
The x'-coordinates, resp. y'-coordinates of the footprint are multiplied
by these factors.
zxscaletablefile, zyscaletablefile:
The x'-coordinates, resp. y'-coordinates of the footprint are multiplied
by these factors. The factors are given as tables in external files.
The format is: first colume z-coordinate, second column the scaling.
inside:
Flag, specifying whether cells inside of the ggcylinder
should be assigned material index MAT, or
whether the cells outside of it should be changed.
show:
Flag, specifying whether an outline of the specified
ggcylinder should be displayed.
If show=off, no outline will be displayed.
If show=later,
the outline will be shown later together
with other specified
bricks, gccylinders, ggcylinders and gbors.
If show=all,
the outlines of all
bricks, gccylinders, ggcylinders and gbors
so far where show was not off
will be displayed.
fixpoints
Enshure meshplanes at the points of the footprint, both at the beginning
and the end of the extrusion range.
point= (XI, YI):
XI, YI are the coordinates of the i.th point in the polygon
that describes the footprint of the ggcylinder.
There have to be minimum 3 points,
or 2 points and an arc
or 2 points and an ellipse.
arc:
(optional):
Indication, that there should be a circular arc from the point that
was specified before to the point that
will be specified as next point.
In order to determine the arc between two points, three parameters
are necessary: The radius of the arc, whether the connection is clockwise
or counterclockwise, and whether the connection should take the large path
or the small path.
radius= RADIUS:
The points are to be connected by an arc with radius=RADIUS
size= [small | large] (optional):
Indication, whether the the connection between the two points should be
on the smaller or the larger side of the arc.
type= [clockwise | counterclockwise]:
Indication, whether the connection between the two points should
proceed clockwise or counterclockwise along the arc.
clear:
Clears the current polygon path.
doit:
Puts the current data as the data of a general cylinder into the meshing
database.
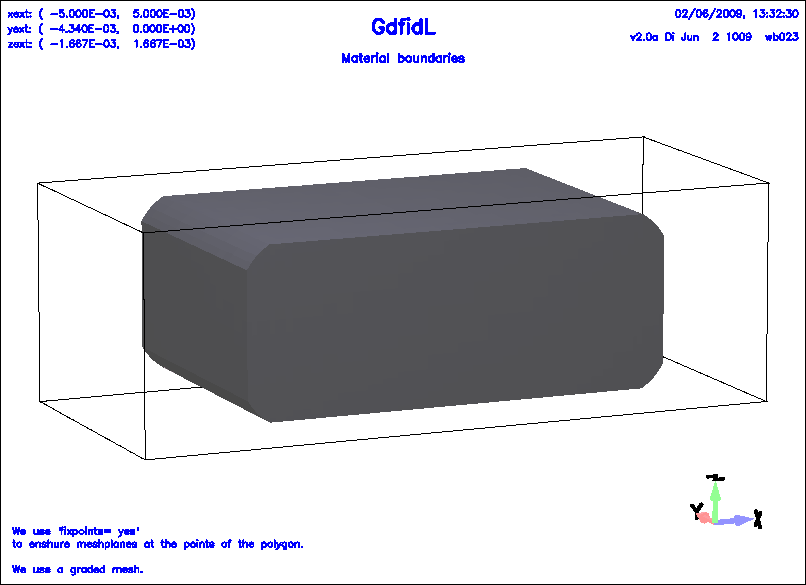
Example
The following decribes a cavity with rounded corners.
# /usr/local/gd1/examples-from-the-manual/ggcylinder-example.gdf
-general
outfile= /tmp/UserName/example
scratch= /tmp/UserName/scratch
text()= We use 'fixpoints= yes'
text()= to enshure meshplanes at the points of the polygon.
text()=
text()= We use a graded mesh.
-mesh
spacing= 100.0e-06
graded= yes, dmaxgraded= 263.3e-06
pxlow= -5e-03, pxhigh= 5e-03
pylow= -4.34e-03, pyhigh= 0
pzlow= -1.6665e-03, pzhigh= 1.6665e-03
cxlow= ele, cxhigh= mag
cylow= ele, cyhigh= mag
czlow= ele, czhigh= ele
-ggcylinder
material= 7
originprime= ( 0, 0, 0 )
xprimedirection= ( 1, 0, 0 )
yprimedirection= ( 0, 0, 1 )
range= ( -4.2e-03, 4.2e-03 )
clear # clear the polygon-list, if any
point= ( -3.3405e-03, -816.5e-06 )
arc, radius= 500.0e-06, type= counterclockwise, size= small
point= ( -2.8405e-03, -1.3165e-03 )
point= ( 2.8405e-03, -1.3165e-03 )
arc
point= ( 3.3405e-03, -816.5e-06 )
point= ( 3.3405e-03, 816.5e-06 )
arc
point= ( 2.8405e-03, 1.3165e-03 )
point= ( -2.8405e-03, 1.3165e-03 )
arc
point= ( -3.3405e-03, 816.5e-06 )
fixpoints= yes # enshure mesh-planes at the points of the polygon
doit
-volumeplot
scale= 4
doit
Figure 1.4:
A simple ggcylinder
 |
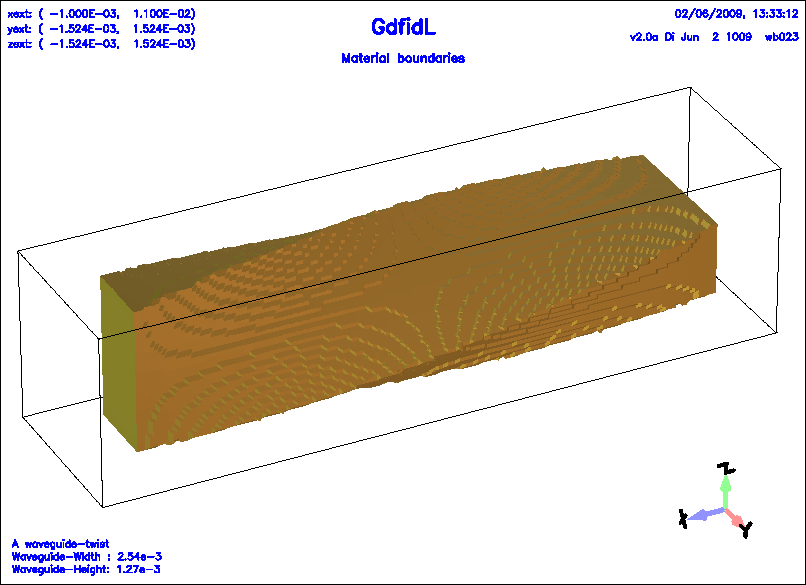
Example
The following decribes a twisted rectangular waveguide.
# /usr/local/gd1/examples-from-the-manual/ggcylinder-twisted.gdf
define(LargeNumber, 10000)
define(LENGTH, 10e-3)
define(WGW, 2.54e-3 )
define(WGH, WGW/2 )
-general
outfile= /tmp/UserName/example
scratch= /tmp/UserName/scratch
text()= A waveguide-twist
text()= Waveguide-Width : WGW
text()= Waveguide-Height: WGH
-mesh
spacing= WGW/40
pxlow= -1e-3, pxhigh= LENGTH+1e-3
pylow= -WGW*0.6, pyhigh= 0.6*WGW
pzlow= -WGW*0.6, pzhigh= 0.6*WGW
define(EL, 10)
-material, material= EL, type= electric
-brick
#
# Fill the universe with metal:
#
material= EL
volume= ( -LargeNumber, LargeNumber, \
-LargeNumber, LargeNumber, \
-LargeNumber, LargeNumber )
doit
-ggcylinder
#
# The twisted waveguide.
# We use a rectangular footprint,
# and specify a pitch.
# The footprint shall rotate by -90 degrees, over a length of LENGTH.
#
material= 0
originprime= ( 0, 0, 0 )
xprimedirection= ( 0, 1, 0 )
yprimedirection= ( 0, 0, 1 )
range= ( 0, LENGTH )
pitch= -90/LENGTH
clear # clear the previous polygon-list, if any
point= ( -WGW/2, -WGH/2 )
point= ( WGW/2, -WGH/2 )
point= ( WGW/2, WGH/2 )
point= ( -WGW/2, WGH/2 )
doit
-volumeplot
eyeposition= ( 1, 2, 1.3 )
scale= 4.5
doit
Figure 1.5:
A simple ggcylinder, with a pitch.
 |
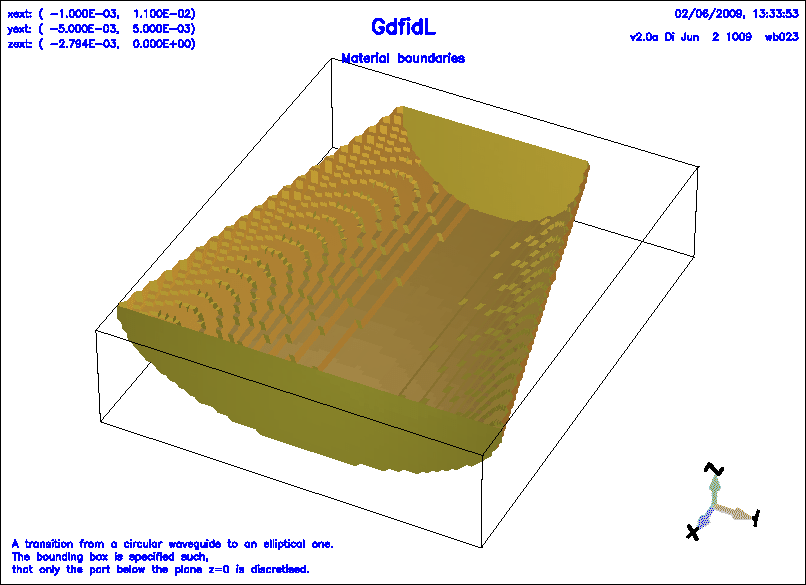
Example
The following decribes a transition from a circular waveguide to
an elliptical waveguide.
# /usr/local/gd1/examples-from-the-manual/ggcylinder-circular-to-elliptic.gdf
define(LargeNumber, 10000)
define(LENGTH, 10e-3)
define(RADIUS1, 2.54e-3 ) define(RADIUS2, 5.0e-3 )
-general
outfile= /tmp/UserName/example
scratch= /tmp/UserName/scratch
text()= A transition from a circular waveguide to an elliptical one.
text()= The bounding box is specified such,
text()= that only the part below the plane z=0 is discretised.
-mesh
spacing= RADIUS1/20
pxlow= -1e-3, pxhigh= LENGTH+1e-3
pylow= -RADIUS2*1.0, pyhigh= RADIUS2*1.0
pzlow= -RADIUS1*1.1, pzhigh= 0
define(EL, 10)
-material, material= EL, type= electric
-brick
#
# Fill the universe with metal:
#
material= EL
volume= ( -LargeNumber, LargeNumber, \
-LargeNumber, LargeNumber, \
-LargeNumber, LargeNumber )
doit
-ggcylinder
#
# The waveguide.
# We use a circular footprint,
# and specify a slope, different in x- and y
#
material= 0
originprime= ( 0, 0, 0 )
xprimedirection= ( 0, 1, 0 )
yprimedirection= ( 0, 0, 1 )
range= ( 0, LENGTH )
# xlingro 1+(RADIUS2/RADIUS1-1)/LENGTH
xslope= (RADIUS2/RADIUS1-1)/LENGTH
yslope= 0
clear # clear the previous polygon-list, if any
point= ( -RADIUS1, 0 )
arc, radius= RADIUS1, size= large, type= counterclockwise
point= ( RADIUS1, 0 )
arc
point= ( -RADIUS1, 0 )
doit
-volumeplot
eyeposition= ( 2, 1, 1.8 )
scale= 3
doit
Figure 1.6:
A simple ggcylinder, with different growthfactors for x and y.
 |
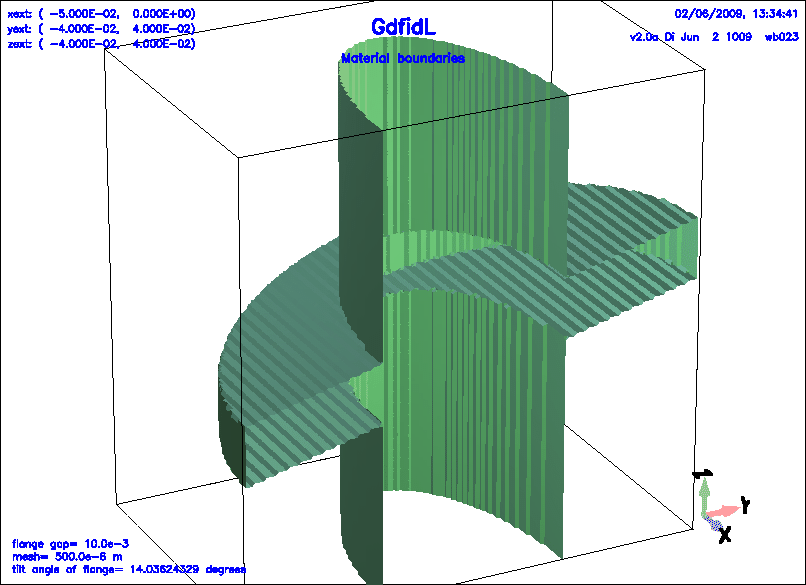
Example
The following decribes a elliptical wedge where the axis of the ggcylinder
is in the z-direction, while the plane normal of the wedge is titled.
# /usr/local/gd1/examples-from-the-manual/ggcylinder-usezprimedirection.gdf
#
# Some helpful symbols:
#
define(EL, 1) define(MAG, 2)
define(INF, 1000)
define(STPSZE, 0.5e-3) # define the transverse mesh step size, 0.5 mm
#
# description of the flange geometry
#
# define(FlangeGap, 2e-3 ) # gap of the flange joint
define(FlangeGap, 10e-3 ) # gap of the flange joint
define(FlangeD0, 80e-3) # diameter of gasket seal
define(Width, FlangeGap/2 ) # 1/2 width of flange gap in z-axis
define(FlangeRadius, FlangeD0/2 )
define(AxisA , 70e-3/2 ) # 1/2 *major diameter of interior ellipse
define(AxisB , 32e-3/2 ) # 1/2 *minor diameter of interior ellipse
#--- parameters related to a tilted flange joint ---
define(ZW, 10e-3) # z-deviation from the y-axis
define(Theta, atan(ZW/FlangeRadius) ) # angle between y-axis and y'-axis
define(RR, FlangeRadius/cos(Theta) ) # radius of tilted cylinder
define(LL, Width/cos(Theta) ) # half length of tilted cylinder
###
### We enter the section "-general"
### Here we define the name of the database where the
### results of the computation shall be written to.
### (outfile= )
### We also define what names shall be used for scratchfiles.
### (scratchbase= )
###
-general
outfile= /tmp/UserName/bla
scratch= /tmp/UserName/scratch-
text()= flange gap= FlangeGap
text()= mesh= STPSZE m
text()= tilt angle of flange= eval(Theta*180/@pi) [degrees]
###
### We define the default mesh-spacing,
### we define the borders of the computational volume.
###
define(Zmin, -4e-2)
define(Zmax, 4e-2)
-mesh
spacing= STPSZE
pxlow= -5e-2, pxhigh= 0
pylow= -4e-2, pyhigh= 4e-2
pzlow= Zmin, pzhigh= Zmax
#####
# Specify that the material index '3'
# describes a perfect conducting material.
-material
material= 3
type= electric
##
## fill the universe with metal
##
-brick
material= 3
xlow= -INF, xhigh= INF
ylow= -INF, yhigh= INF
zlow= -INF, zhigh= INF
doit
##
## Step 1: carve out a tilted circular box
##
-ggcylinder # a parallelogram gap with a tilt angle
material= 0
origin= (0,0,0)
xprimedirection= (1,0,0)
yprimedirection= (0, cos(Theta), sin(Theta) )
zprimedirection= ( 0, 0, 1 )
usezprimedirection= yes
range= ( -LL, LL )
clear
point= ( -RR, 0 )
arc, radius= RR,type= counterclockwise, size= small
point= ( RR, 0 )
arc, radius= RR,type= counterclockwise, size= smal
point= ( -RR, 0 )
show= later
doit
usezprimedirection= no # Switch back to the default, 'no'
##
## Step 2: Creating the interior footprint of elliptic beampipe(hollow)
##
-ggcylinder
material= 0
origin= (0, 0, 0)
xprimedirection= (1, 0, 0)
yprimedirection= (0, 1, 0)
range= (Zmin-2*STPSZE, Zmax+STPSZE)
xslope= 0, yslope= 0
clear # clear any old polygon-description of the footprint
# point= (x', y')
point= (0, -AxisB),
ellipse, center= (0,0),
point= (AxisA, 0),
ellipse,
point= (0, AxisB),
ellipse,
point= (-AxisA, 0),
ellipse,
point= (0, -AxisB),
# show= all
doit
############
-volumeplot
eyeposition= ( 1, -0.5, 0.5 )
scale= 3
doit
Figure 1.7:
A simple ggcylinder, with zprimedirection different from the footprints plane normal.
 |
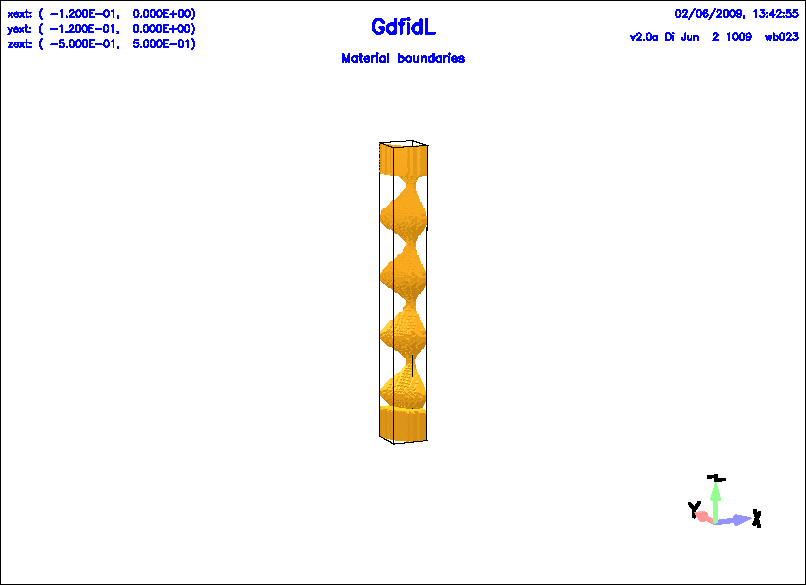
Example
The following decribes a corrugated waveguide. The cross-section is specified as a
ggcylinder, the cross section is circular. The xscale and yscale is specified via
tables.
# /usr/local/gd1/examples-from-the-manual/zxscale-example.gdf
## beginning of structure modeling
##
define(FFAC, 1)
define(BunchLength, 2e-2) # rms bunch length of Gaussian beam
define(Radius, eval(240.03e-3/2) ) # Radius of circle
define(TaperLength, 374.93e-3) # Length of the taper
define(AxisA, eval(80e-3/2) ) # Radius a of the ellipse
define(AxisB, eval(38e-3/2) ) # Radius b of the ellipse
define(PipeLength, 6e-2) # Length of elliptic beampipe
define(CircularPipe, 20e-2) # Half length of circular beampipe
define(STPSZE, eval(BunchLength/5/FFAC) ) # Mesh size
define(FMAX, 2e9) # Max. frequency of interest in [Hz]
define(MAXSPACING, eval(3e8/FMAX/20) )
-general
outfile= /tmp/UserName/bla
scratch= /tmp/UserName/scratch-
-mesh
spacing= 2*STPSZE
pxlow = -Radius, pxhigh= 0
pylow = -Radius, pyhigh= 0
pzlow= -0.5, pzhigh= 0.5
zfixed( 2, -(TaperLength+CircularPipe), -CircularPipe )
zfixed( 2, CircularPipe, CircularPipe+TaperLength )
#
# The conditions to use at the borders of the computational volume:
#
cxlow= electric, cxhigh= magnetic
cylow= electric, cyhigh= magnetic
czlow= electric, czhigh= electric
define(CircularPipe, 200e-2) # Half length of circular beampipe
# Fill the universe with metal.
-brick
material= 1
volume= ( -INF,INF, -INF,INF, -INF,INF )
doit
##
## Create the circular beampipe, with corrugation.
##
-ggcylinder
material= 0
origin= (0,0, -0.4 )
xprimedirection= (1,0,0)
yprimedirection= (0,1,0)
range= (0, 0.8 )
xslope= 0
yslope= 0
zxscale= zxscale-sinus
zyscale= zxscale-sinus
clear # clear any old polygon-description of the footprint
# point= (x', y')
point= (0, -Radius)
arc, radius= Radius, type= clockwise, size= small
point= (0, Radius)
arc
point= (0, -Radius)
# show= now
doit
-gccylinder
material= 0, radius= Radius, length= INF
origin= ( 0, 0, 0.4 ), direction= ( 0, 0, 1 ), doit
origin= ( 0, 0, -0.4 ), direction= ( 0, 0, -1 ), doit
-volumeplot, doit
Figure 1.8:
The discretisation of a corrugated circular waveguide, specified as a ggcylinder with zxscale.
 |



Next: -gbor: A general body
Up: Geometric primitives
Previous: -gccylinder: A circular cylinder
Contents




